RESEARCH
[Publication] Commensal consortia decolonize Enterobacteriaceae via ecological control
September 19, 2024
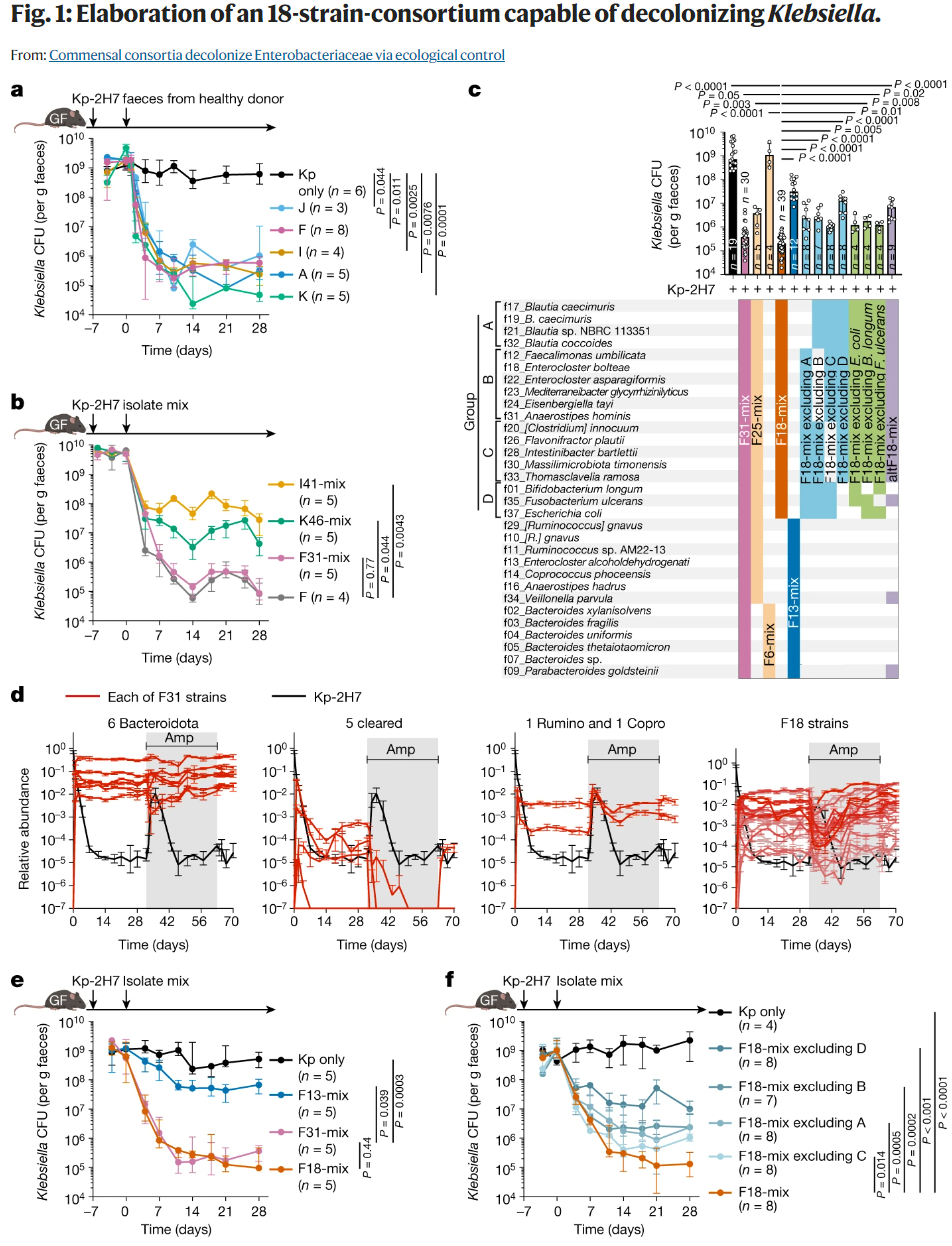
Fig.1: Elaboration of an 18-strain-consortium capable of decolonizing Klebsiella.
| Title |
Commensal consortia decolonize Enterobacteriaceae via ecological control |
|---|---|
| Authors | Munehiro Furuichi [1],[2],[14]; Takaaki Kawaguchi [1],[2],[14]; Marie-Madlen Pust [3],[4],[14]; Keiko Yasuma-Mitobe [1],[14]; Damian R. Plichta [3]; Naomi Hasegawa [1]; Takashi Ohya [1],[2]; Shakti K. Bhattarai [5]; Satoshi Sasajima [1]; Yoshimasa Aoto [6]; Timur Tuganbaev [1],[7]; Mizuki Yaginuma [1]; Masahiro Ueda [2],[6]; Nobuyuki Okahashi [2],[8],[9]; Kimiko Amafuji [6]; Yuko Kiridoshi [6]; Kayoko Sugita [1]; Martin Stražar [3]; Julian Avila-Pacheco [3]; Kerry Pierce [3]; Clary B. Clish [3]; Ashwin N. Skelly [1]; Masahira Hattori [2],[10]; Nobuhiro Nakamoto [11]; Silvia Caballero [12]; Jason M. Norman [12]; Bernat Olle [12]; Takeshi Tanoue [1],[2]; Wataru Suda [2],[10]; Makoto Arita [2],[7],[9]; Vanni Bucci [5]; Koji Atarashi [1],[2],[7]; Ramnik J. Xavier [3],[4],[13] & Kenya Honda [1],[2],[7] |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07960-6 |
| Journal | Nature |
| Vol/Num/Page | 633, 878–886 (2024) |
| Published Date | 18 September 2024 |
Affiliations:
[1] Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Keio University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan.
[2] RIKEN Center for Integrative Medical Sciences, Yokohama, Japan.
[3] Infectious Disease and Microbiome Program, Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, Cambridge, MA, USA.
[4] Center for Computational and Integrative Biology, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA.
[5] Department of Microbiology and Physiological Systems, Program in Microbiome Dynamics, UMass Chan Medical School, Worcester, MA, USA.
[6] JSR-Keio University Medical and Chemical Innovation Center, Keio University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan.
[7] Human Biology Microbiome Quantum Research Center (Bio2Q), Keio University, Tokyo, Japan.
[8] Department of Bioinformatic Engineering, Graduate School of Information Science and Technology, Osaka University, Osaka, Japan.
[9] Division of Physiological Chemistry and Metabolism, Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Keio University, Tokyo, Japan.
[10] Cooperative Major in Advanced Health Science, Graduate School of Advanced Science and Engineering, Waseda University, Tokyo, Japan.
[11] Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Keio University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan.
[12] Vedanta Biosciences, Cambridge, MA, USA.
[13] Department of Molecular Biology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA, USA.
[14] These authors contributed equally: Munehiro Furuichi, Takaaki Kawaguchi, Marie-Madlen Pust, Keiko Yasuma-Mitobe.
More Bio2Q News
【2/19 Seminar】WPI-Bio2Q Open Seminar: Takeharu Mino, Ph.D.
Keio University Human Biology-Microbiome-Quantum Research Center (WPI-Bio2Q) will hold a seminar as follows. This is an event for faculty, ...
【3/31 Seminar】WPI-Bio2Q Open Seminar: The 173rd Brain Club Mini-symposium
Keio University Human Biology-Microbiome-Quantum Research Center (WPI-Bio2Q) will hold a seminar as follows. This is an event for faculty, ...
【Event Report】 Future Scientists Visit Bio2Q: Field Trip for Tokyo Gakugei Unive...
On February 5, 2026, the WPI-Bio2Q Research Center at Keio University hosted a science field trip for 25 first-year students from Tokyo Gaku...
【2/25Seminar】WPI-Bio2Q Open Seminar: Andrew Wray, PhD
Keio University Human Biology-Microbiome-Quantum Research Center (WPI-Bio2Q) will hold a seminar as follows. This is an event for faculty, ...
Two New Titles Released in the “Booklets Series for Young Readers” : Issue 09 (T...
The Digital Booklet Series for Young Readers, which introduces research activities at Bio2Q, has added two new issues. Issue 09 features ...