イベント
【公開セミナー】Tsutomu Suzuki, Ph.D.
2024年9月11日

Tsutomu Suzuki, Ph.D.
Credits: WPI-Bio2Q

セミナーの様子
Credits: WPI-Bio2Q

Credits: WPI-Bio2Q

ポスター
Credits: WPI-Bio2Q








慶應義塾大学ヒト生物学-微生物叢-量子計算研究センター(WPI-Bio2Q)は、以下のとおり、公開セミナーを開催しました。
| 日時 | 2024年9月10日(火)16:00 -17:30 |
|---|---|
| 場所 | 慶應義塾大学信濃町キャンパス総合医科学研究棟1Fラウンジ(現地開催のみ) |
| 演題 | RNA Modifications in Health and Disease |
| 講演者 | Tsutomu Suzuki, Ph.D. Professor, Department of Chemistry and Biotechnology, University of Tokyo |
| 言語 | 英語 |
講演要旨
RNA molecules frequently undergo post-transcriptional modifications, which are essential for their proper function. To date, about 150 different types of chemical modifications have been identified in various RNA molecules across all domains of life. There are still a number of novel modifications to be discovered. RNA modifications appear to confer chemical diversities to simple RNA molecules basically composed of four letters, to acquire a greater variety of biological functions. These modifications play critical roles in stability and functions of RNA molecules. The physiological importance of RNA modification has been demonstrated by human diseases caused by aberrant RNA modification. We reported a severe reduction in the frequency of tRNA modifications in mitochondrial disease patients, like MELAS and MERRF. These findings provided the first evidence of RNA modification disorder. We have termed “RNA modopathy” as a new category of human diseases.
Queuosine (Q), a tRNA modification characterized by a 7-deazaguanosine with a bulky side chain, is widely present in both bacteria and eukaryotes. Unique to this modification, the free base of Q, known as queuine, is incorporated through a base replacement reaction, converting guanine (G) to Q. Eukaryotes, including humans, cannot synthesize queuine and must obtain it as a dietary nutrient from gut microbiota or dietary sources. In humans and other vertebrates, Q can be further modified by glycosylation, forming either galactosyl-queuosine (galQ) or mannosyl-queuosine (manQ). The function of these glycosylated Q modifications remained unclear for nearly half a century after their discovery. Recently, we identified two glycosyltransferases responsible for the formation of galQ and manQ and elucidated the biosynthesis, functional roles in protein synthesis, and physiological significance of these glycosylated Q tRNA modifications.
ニュースをさらに見る:
【3/16セミナー】WPI-Bio2Q Open Seminar: 于 毅寛
世界トップレベル研究拠点(WPI)慶應義塾大学ヒト生物学-微生物叢-量子計算研究センター(Bio2Q)は以下のとおり公開セミナーを開催いたします。 慶應義塾関係者の方であれば、どなたでもご参加いただけます。 日時 2026年3月16日 (月) 14:00~1...
【セミナー報告】WPI-Bio2Q 公開 Seminar: Ping-Chih Ho, PhD
世界トップレベル研究拠点(WPI)慶應義塾大学ヒト生物学-微生物叢-量子計算研究センター(Bio2Q)は以下のとおり公開セミナーを開催しました。 日時: 2026年3月5日 (木) 17:00~18:00 会場:慶應義塾大学信濃町キャンパス 総合医科学研究棟 6階会議...
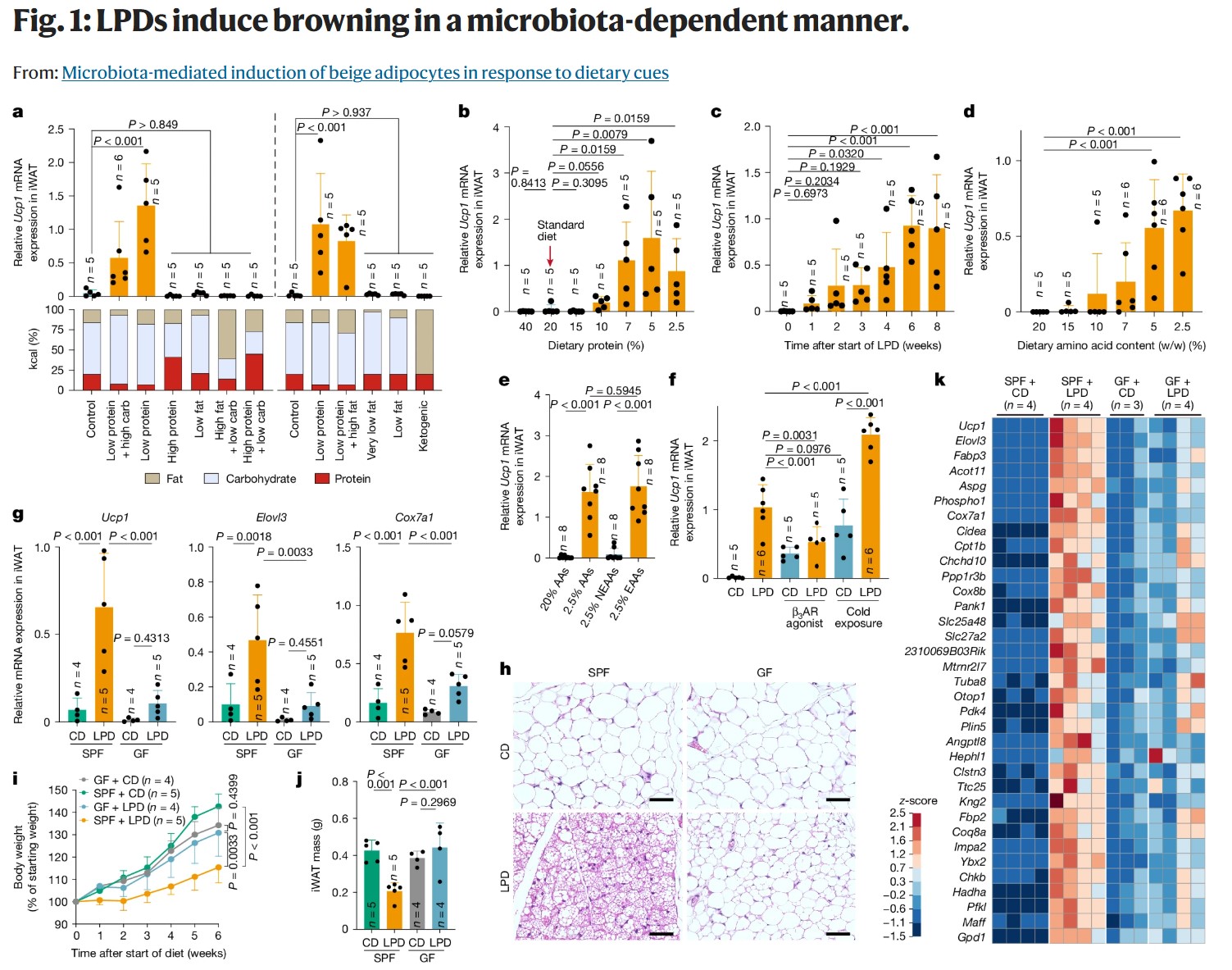
【研究成果】食餌シグナルによる腸内細菌を介したベージュ脂肪細胞の誘導メカニズムを解明
Bio2Q拠点長の本田賢也教授らのグループは、低タンパク質食が腸内細菌を介して、エネルギーを消費する「ベージュ脂肪細胞」を誘導する仕組みを解明しました。ヒトから特定した4つの菌株が、胆汁酸代謝やアンモニア産生を通じて肝臓や脂肪組織のネットワークに作用し、代謝を改善することを突き止...
【3/12セミナー】WPI-Bio2Q Open Seminar: Arjun S. Raman, PhD
世界トップレベル研究拠点(WPI)慶應義塾大学ヒト生物学-微生物叢-量子計算研究センター(Bio2Q)は以下のとおり公開セミナーを開催いたします。 慶應義塾関係者の方であれば、どなたでもご参加いただけます。 日時 2026年3月12日 (木) 15:00~1...
【4/3セミナー】WPI-Bio2Q Open Seminar: Damian R. Plichta, PhD
世界トップレベル研究拠点(WPI)慶應義塾大学ヒト生物学-微生物叢-量子計算研究センター(Bio2Q)は以下のとおり公開セミナーを開催いたします。 慶應義塾関係者の方であれば、どなたでもご参加いただけます。 日時 2026年4月3日 (金) 14:00~15...